Heavy Equipment Safety – Comprehensive Guide

Heavy equipment is a vital part of modern construction and industrial projects, from building skyscrapers to paving roads or removing essential materials like earth from the ground. Without the right machines, tasks like creating landscapes, moving large amounts of materials, or preparing job sites would be nearly impossible. But this power comes with a high risk, poorly managed heavy equipment poses dangers like accidents, injuries, and even fatalities.
The construction industry relies on strict protocols to mitigate risks. For example, OSHA standards emphasize proper training for operators handling heavy equipment, ensuring they’re used safely even in complex scenarios like industrial material extraction. In my years overseeing job sites, I’ve seen how skipping steps like ignoring ground stability checks or failing to inspect materials-handling machinery leads to preventable accidents. OSHA’s focus on high-visibility PPE, routine maintenance, and hazard communication tackles these risks head-on, blending regulation with practicality.
The Importance of Heavy Equipment Safety
OSHA’s Role in Reducing Heavy Equipment Risks
In 2019, 20% of the 5,333 worker deaths reported in the U.S. occurred in construction, with two-thirds of accidents tied to the “fatal four”: falls, struck by object, electrocutions, and caught in-between. Three of these causes routinely occur near or on heavy equipment. As someone who’s witnessed a swinging crane hook nearly strike a worker a disaster avoided only because the team followed OSHA protocols—I can’t stress enough how safety standards save lives.
Breaking Down the “Fatal Four”
Falling from height or off construction equipment remains a top risk. Electrocutions often happen when workers are accidentally energized by live electricity, while caught in-between incidents involve components of machinery or materials crushing limbs. Free-falling objects like tools dropped from scaffolding are another silent killer. OSHA’s reports emphasize proper training, securing loads, and lockout / tag out procedures to prevent these accidents.
Why Companies Must Prioritize Safety Culture
Construction companies that acknowledge the importance of heavy equipment safety see fewer deaths and injuries. Simple steps—like inspecting equipment before use, marking hazard zones, and enforcing PPE rules—can stop hit-by incidents or machinery malfunctions. I’ve seen crews transform from chaotic to compliant by treating OSHA guidelines as non-negotiable, not optional. When safety becomes a reflex, not a checklist, everyone goes home alive.
Heavy Equipment Safety – OSHA Guidelines for Risk-Free Operations
OSHA heavy equipment safety standards aren’t just rules they’re lifelines. Over my years on construction sites, I’ve seen how ignoring basics like three-point contact or seatbelt use turns routine tasks into disasters. Let’s break down practices that keep operators and crews safe.
Start with Pre-Operation Checks and Training
Never skip the inspection phase. A thorough ground-level walk around to check for leaks, loose items, or fluid issues can prevent 80% of onsite hazards. Pair this with specialized training especially for inexperienced operators—to handle complex operations safely. OSHA emphasizes knowing your machine’s blind spots; I’ve watched spotters save lives by guiding operators around stray workers in busy construction zones.
Protect Yourself and Your Team
PPE isn’t optional. Steel-toed boots, gloves, and eye protection shield against flying debris, while a respirator becomes critical in dusty environments. Always wear a seatbelt even on “short” drives across rough terrain. Fatigue is a silent killer: recognize your limits during intense heat or emotionally draining shifts. If medications cause drowsiness, step back.
Communication and Spatial Awareness save Lives
Hand signals are the universal language on a job site. Train everyone to indicate movement clearly confusion here leads to crushed objects or worse. Use buffer zones to keep workers clear of danger zones, and rely on spotters for clearances checks. I’ve seen a single misstep in safe operation zones result in weeks of downtime.
Heavy Equipment Safety – Building a Culture of Prevention
When I first stepped onto a construction site, the chaos of moving machinery made me realize how vital occupational safety truly is. OSHA heavy equipment safety standards aren’t just rules—they’re lifelines. These guidelines enforce safety protocols like proper heavy equipment operation, regular inspections, and risk mitigation strategies to address workplace hazards. I’ve seen crews transform when they prioritize accident prevention through adequate training. For example, simple practices like pre-shift equipment checks or clear communication channels can drastically reduce incidents. But compliance isn’t a checkbox; it’s about embedding safety compliance into daily routines.
Elevating Standards with Professional Heavy Equipment Safety Training
This is where Safety Pro consultants shine. Early in my career, a near-miss with an excavator taught me that refresher training isn’t optional—it’s essential. Professional training programs from Safety Pro don’t just meet construction site safety norms; they exceed them. Their courses blend hands-on heavy equipment safety drills with equipment safety theory, ensuring workers grasp both the “how” and “why” of protocols. One game-changer I’ve observed is their focus on workplace hazards specific to high-risk zones, like uneven terrain or blind spots. By equipping teams with resources like scenario-based learning and real-time feedback, they keep workers safe while fostering a safe environment.
Regulatory Landscape Comparison
OSHA vs. NIOSH Approaches to Heavy Equipment Safety

| Authority | Approach | Key Tools | Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|---|
| OSHA | Regulatory enforcement through standards and inspections | CFR 29 CFR 1926.600 (equipment), 1926.602 (material handling) | Equipment design, operator qualifications, pre-operation checks |
| NIOSH | Research-driven guidelines and toolbox talks | Construction Toolbox Talks series | Hazard awareness, visibility studies, case-study learning |
While OSHA sets mandatory standards—with citations, fines, and formal enforcement—NIOSH focuses on translating research into actionable training tools, raising awareness of risks like blind spots and equipment visibility. Together, they form a robust framework for safeguarding workers.
Key Insights for Next-Level Safety
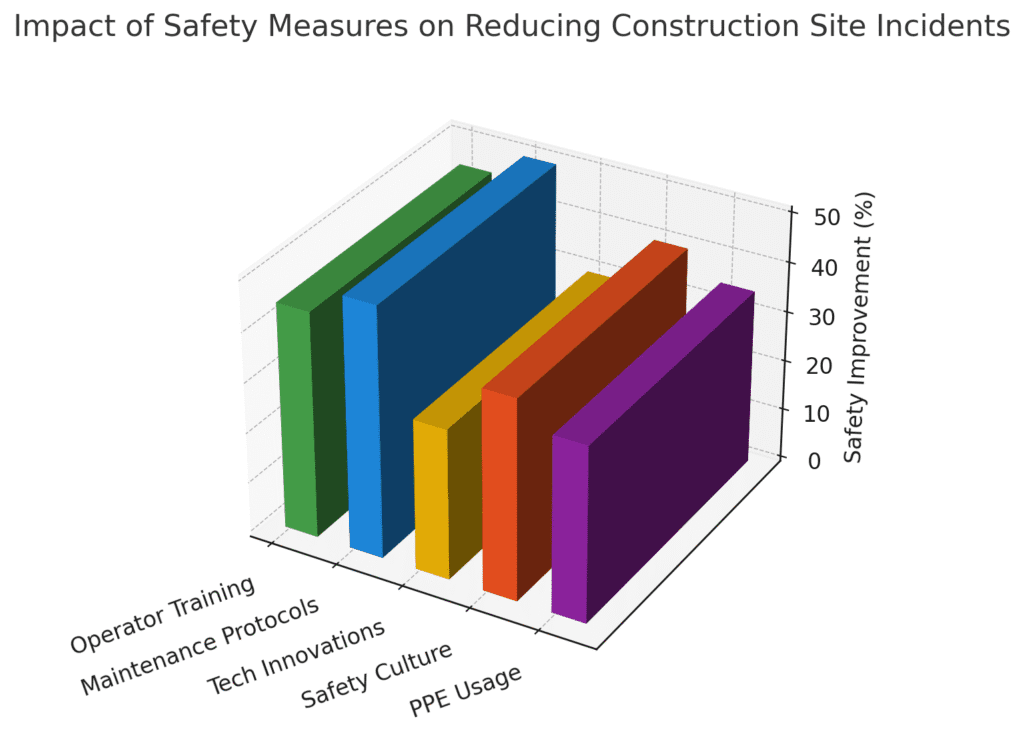
1. Operator Training & Competency

Effective training goes beyond showing a manual; it immerses operators in realistic scenarios. Simulator-based programs—like those offered by leading OEMs—allow trainees to practice pre-operation walkarounds and emergency procedures in a risk-free environment. Integrating adult-learning techniques such as interactive toolbox talks can boost retention by up to 40%. Combining OSHA’s formal qualifications with NIOSH’s Toolbox Talks ensures operators not only know the rules but live them.
2. Maintenance & Inspection Protocols

A rigorous inspection regimen catches hazards before they escalate. Standard pre-start checklists should include:
- Fluid levels and leaks
- Proper function of controls and brakes
- Condition of Rollover Protection Structures (ROPS)
- Secure cab glass and mirrors
Implementing lockout-tagout procedures during servicing prevents accidental start-ups and reduces maintenance injuries by over 50%.
3. Technological Innovations
Advances in telematics, proximity detection, and 360° camera systems have revolutionized hazard awareness. Studies show that real-time alerts can cut near-miss incidents by 30%. From wearable sensors that monitor operator fatigue to machine-learning platforms predicting component failures, technology offers an extra layer of protection when integrated into standard practices.
4. Building a Safety Culture

Policies mean little without buy-in. Encourage front-line feedback through anonymous near-miss reporting apps and recognize crews for safe-work milestones. Personal stories—like the one of Antonio, a day laborer who suffered life-altering injuries after a contractor ignored fall-protection rules—underscore the human cost of complacency. The Guardian Leadership’s visible commitment to safety, combined with regular “safety stand-downs,” fosters an environment where every worker feels empowered to speak up.
Essential Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
| PPE Item | Purpose | Standard/Guideline |
|---|---|---|
| Hard Hat | Protect from falling objects | OSHA 29 CFR 1926.100 OSHA |
| High-Visibility Vest | Enhance operator and pedestrian visibility | ANSI/ISEA 107-2020 |
| Safety Boots | Prevent crush and puncture injuries | OSHA 29 CFR 1926.96; ASTM F2413 |
| Gloves | Hand protection and improved grip | ANSI/ISEA 105-2016 |
| Hearing Protection | Reduce noise-induced hearing loss | OSHA 29 CFR 1926.101; NIOSH Criteria Document |

Proper fit, regular inspection, and prompt replacement of PPE are nonnegotiable. Newly effective OSHA rules now require that construction PPE fit workers correctly—an important step toward true protection. OSHA
Conclusion
Heavy equipment safety demands more than compliance—it thrives on continuous improvement, innovation, and a culture that values every individual on the job site. By blending OSHA’s enforcement, NIOSH’s research, cutting-edge technology, and personal accountability, you can transform safety protocols from mere policies into a shared commitment.
What’s your next step? Share your toughest safety challenge in the comments, explore our related posts on equipment maintenance and site hazard management, or subscribe for ongoing insights. Together, let’s raise the bar on heavy equipment safety—one site at a time.
