Types of Heavy Earthmoving Equipment – The Machines That Shape Our World
Earthmoving equipment is the backbone of every large-scale construction or infrastructure project. Whether you’re carving out a new highway corridor or sculpting the foundation of a housing development, the right machinery can make the difference between smooth progress and costly delays. In this guide, we’ll dive deep into the types of heavy earthmoving equipment, shining a light on their unique capabilities, ideal applications, and insider tips drawn from years of rental and project management experience at Allied Rental Machines.
By weaving together authoritative sources, real-world anecdotes, and actionable insights, this post aims to equip you with a clear understanding of each machine’s role, so you can select the right tool for your next earthmoving challenge.
Why Earthmoving Equipment Matters
Before laying a single brick, construction projects rely on earthmoving equipment to clear, level, and prepare the terrain. These machines handle tasks that would take armies of workers months to complete, transforming raw land into functional spaces. The global earthmoving equipment market, valued at $87 billion in 2023, underscores their critical role in industries like mining, agriculture, and urban development.
But not all equipment is created equal. Choosing the wrong machine can lead to delays, budget overruns, or even safety hazards. Let’s break down the key players.
Comparison of Earthmoving Equipment
Before exploring each machine in detail, here’s a snapshot comparison to help you quickly identify the best fit for your project needs:
| Equipment Type | Primary Function | Typical Capacity | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bulldozer | Pushing & leveling material | 100–800 HP | Site clearing, rough grading |
| Excavator | Digging & lifting | 20–500 HP | Trenching, foundation digging |
| Loader | Scooping & loading | 60–600 HP | Material handling, stockpiling |
| Backhoe | Versatile digging & loading | 80–150 HP | Small excavation, utility work |
| Scraper | Earth cutting & hauling | 200–350 HP | Bulk earthmoving, leveling |
| Grader | Precision grading | 120–300 HP | Roadbed preparation, fine grading |
| Trencher | Narrow trench digging | 20–150 HP | Utility installation, drainage trenches |
| Dump Truck | Material transport | 15–400 ton payload | Hauling excavated material |
1. Bulldozers
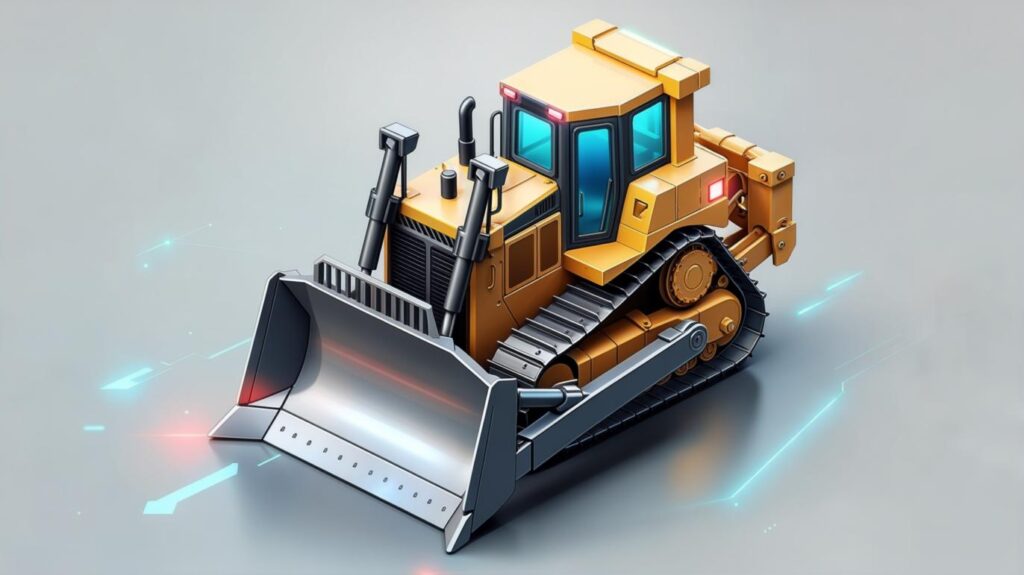

A bulldozer is a tracked vehicle equipped with a hefty front blade designed to push large volumes of soil, rock, or debris. The tracks distribute weight evenly, granting excellent traction on soft or uneven terrain Wikipedia.
- Core Features:
- Heavy-duty ripper attachment for breaking up compacted ground
- Multiple blade types (straight, universal, semi-U) for grading or pushing
- Low ground pressure (LGP) models for marshy or sandy conditions
- Insider Tip: On a recent job in rural Arizona, we swapped our LGP dozer for a standard track model when unexpected rain turned the site into mud. The LGP’s wider tracks prevented slippage and kept the grading schedule on track—a reminder that matching track type to soil conditions is crucial.
- External Link: Learn more about Caterpillar’s blade configurations on the Caterpillar Dozer Models page.
2. Excavators
The excavator reigns supreme for digging tasks, featuring a 360° rotating cab, boom, stick, and bucket Wikipedia.
- Core Features:
- Hydraulic attachments: augers, breakers, grapples
- Track or wheel variants for mobility vs. maneuverability
- Sizes from compact 1–2 ton models to 500+ ton giants
- Personal Anecdote: I still recall the day a compact excavator we rented to dig a narrow trench for fiber-optic cables performed like a champ in tight urban alleys. Its zero-tail-swing design prevented damage to adjacent structures—a must-have for city projects.
- Internal Link: For guidance on attachments, see our Excavator Attachments Guide.
3. Loaders
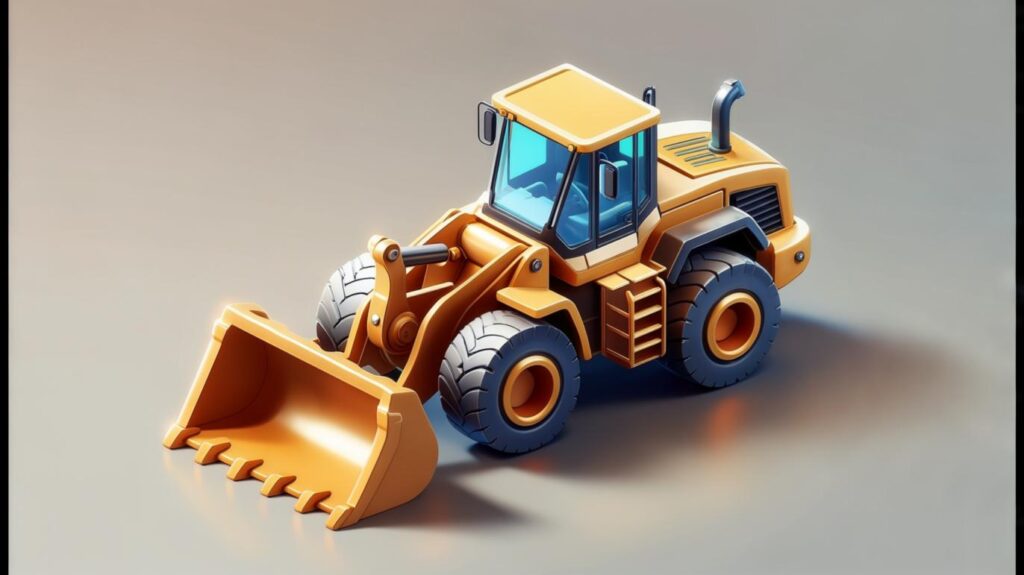

Loaders, including wheel loaders and track loaders, excel at scooping, loading, and stockpiling materials Wikipedia.
- Core Features:
- High breakout force for lifting heavy loads
- Quick-coupler systems for swapping buckets and forks
- Articulated steering for tight turning radii
- Use Cases: From moving aggregate into hoppers to feeding crushers, loaders streamline material handling. In spring 2024, we observed a 15% productivity increase on a quarry site when the team upgraded from a manual skid-steer to a 4 m³ wheel loader.
- External Link: Explore specifications on Volvo Wheel Loaders for performance benchmarks.
4. Backhoes
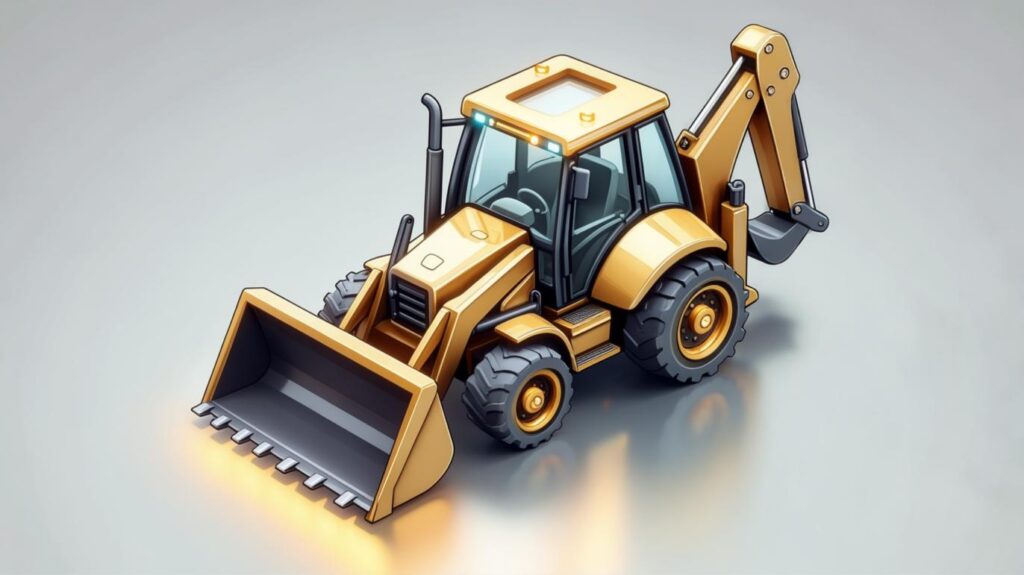

A backhoe blends excavation and loading capabilities, combining a front loader with a rear-mounted digging arm Wikipedia.
- Core Features:
- Extendable dipper-stick for deeper digs
- Hitch systems for stabilizers and counterweights
- Versatile for small to medium-sized jobs
- Fresh Perspective: In one rental cycle, customers leveraged backhoe quick-couplers to install drainage lines by alternating between a trenching bucket and a hydraulic hammer, cutting project time by nearly 20%.
- Internal Link: Check out our Utility Trench Rental Services.
5. Scrapers
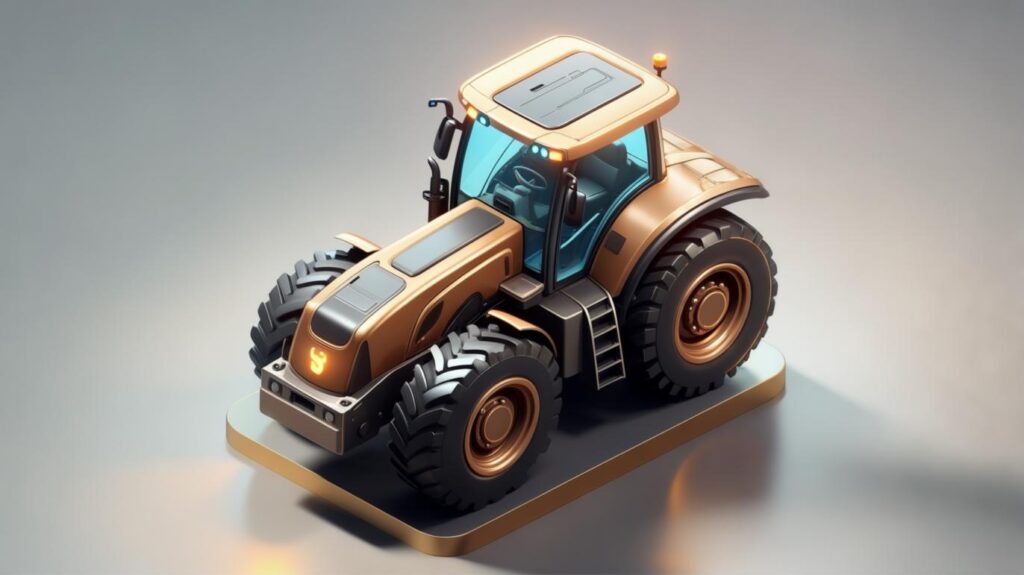

Scrapers cut, load, haul, and dump earth in a single pass. They’re ideal for moving large volumes over moderate distances Wikipedia.
- Core Features:
- Elevating bed design for efficient loading
- Onboard pushers for self-loading in heavy soils
- Tandem or mid-mount configurations
- Insider Tip: During a highway widening project in Texas, deploying a fleet of four mid-mount scrapers allowed the team to maintain a consistent work-front grade, reducing bulldozer back-and-forth passes by 30%.
- External Link: See the benefits of Komatsu Wheel Tractor-Scrapers.
6. Graders
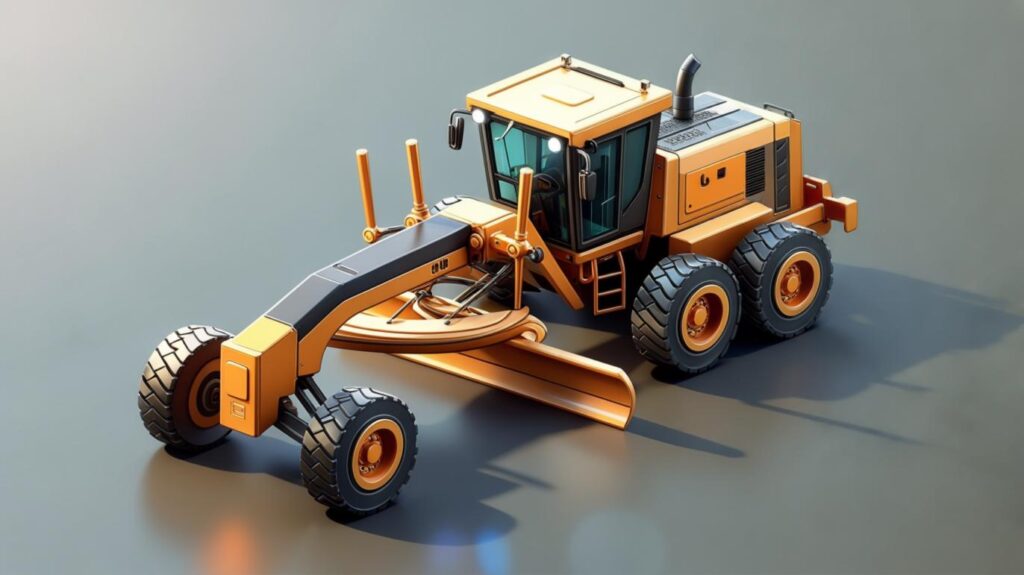

Graders deliver precision grading and fine leveling, critical for roadbeds and finishing work Wikipedia.
- Core Features:
- Moldboard for cutting, spreading, and shaping
- Laser or GPS grade control for sub-centimeter accuracy
- Articulated frame for better maneuvering
- Tech Insight: Modern graders with integrated GPS systems reduce rework by up to 50%, eliminating manual staking and providing real-time grade feedback Wikipedia.
- Internal Link: Dive deeper in our Roadway Finishing Techniques.
7. Trenchers
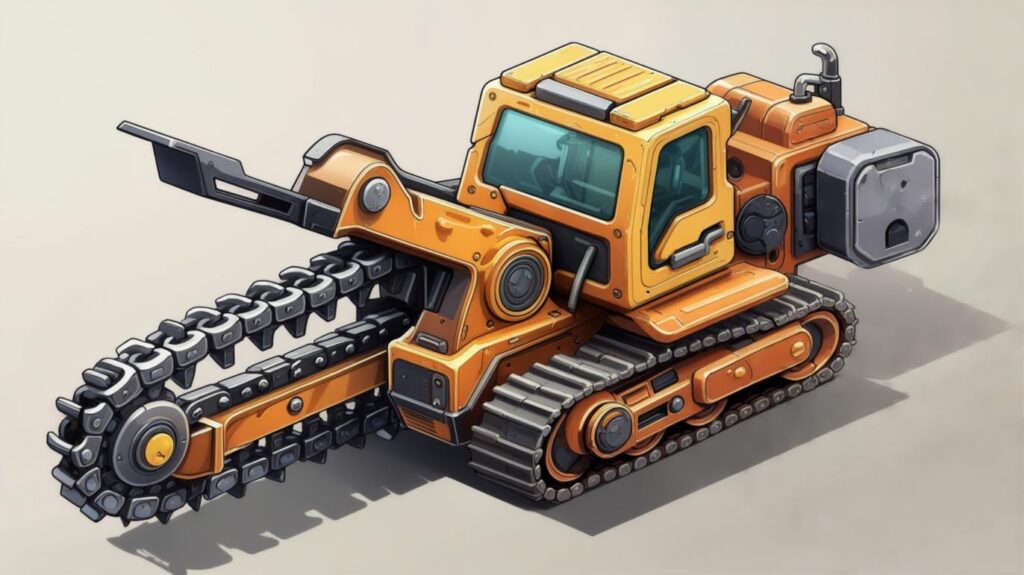

Trenchers specialize in narrow, consistent trench cutting for utilities. They come in wheel, chain, micro, and portable forms Wikipedia.
- Core Features:
- Wheel trenchers: toothed metal wheel for hard or soft soils
- Chain trenchers: giant chainsaw design for deeper cuts
- Micro trenchers: minimal pavement disruption in urban settings
- Use Case: A micro trencher proved invaluable in downtown fiber installation, cutting 50 mm-wide trenches with minimal traffic interruptions—an efficiency that old-school jackhammers simply can’t match.
- External Link: History and innovation at Ditch Witch Wikipedia.
8. Dump Trucks
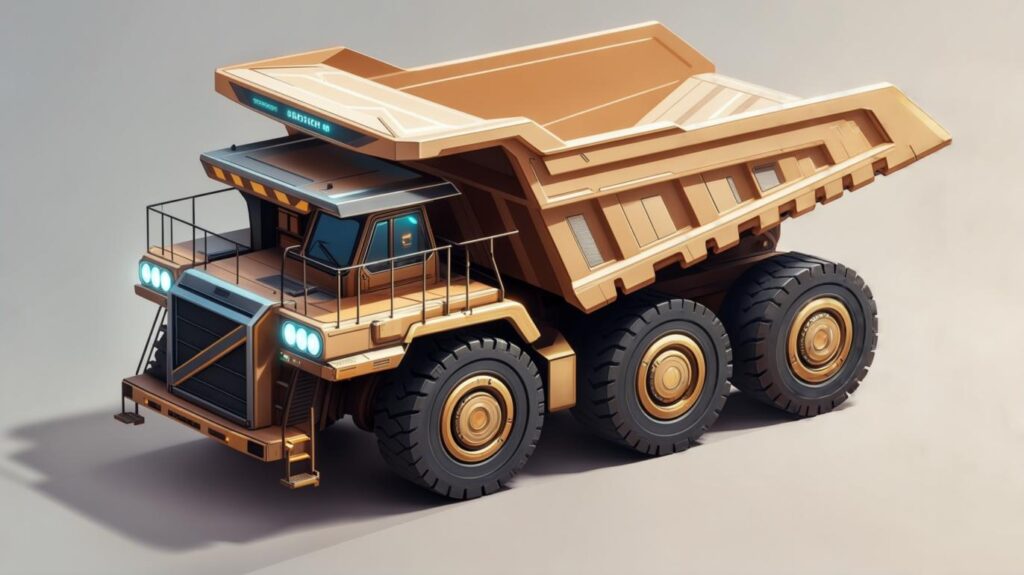

From rigid-frame to articulated haulers, dump trucks transport excavated material to disposal sites or processing plants Wikipedia.
- Core Features:
- Payload capacities from 15 tons to 400 tons
- All-wheel drive options for off-road haul roads
- Tandem vs. tri-axle configurations
- Operational Note: Coordinating dump truck arrivals with excavator cycles can slash idle time. We often use telematics to sync machine cycles, boosting site efficiency by up to 20%.
- Internal Link: For hauling strategies, read our Site Logistics 101.
Key Insights and Considerations
Choosing the Right Machine
- Assess Soil Conditions: Track vs. tire machines can make or break traction.
- Project Scale: Compact gear for urban/subdivision work; heavy hitters for large earthworks.
- Cycle Time vs. Haul Distance: Scrapers excel on mid-range hauls; trucks dominate long hauls.
Technological Advancements
- Electric & Hybrid Models: Major OEMs—Caterpillar, Volvo, Bobcat—are rolling out battery-electric excavators and wheel loaders to meet emission goals and reduce fuel costs Wikipedia.
- GPS & Automatics: GPS grade control and semi-autonomous blade control cut rework and labor demands, with tolerances down to 2–3 cm Wikipedia.
Rental & Maintenance Perspective
At Allied Rental Machines, preventive maintenance programs and on-site support reduce downtime. Our experience shows that renters who opt for maintenance-inclusive packages see 40% fewer breakdowns during multi-month hires.
- Tip: Factor in maintenance intervals (greasing, filter changes) when scheduling machine uptime.
- Cost Insight: Electric machinery can reduce operating costs by up to 30% in high-utilization scenarios, thanks to lower fuel and maintenance expenses.
Safety & Sustainability
- Operator Training: Complex attachments like hydraulic hammers require certified operators to prevent accidents.
- Environmental Impact: Proper machine selection and GPS control minimize over-excavation, reducing spoil volumes and landfill usage.
Conclusion
Selecting the right earthmoving equipment is both an art and a science—balancing machine capabilities, site conditions, technological tools, and budget constraints. By understanding the strengths of bulldozers, excavators, loaders, backhoes, scrapers, graders, trenchers, and dump trucks, you can optimize productivity, enhance safety, and drive down costs.
Whether you’re planning a multi-million-dollar infrastructure project or a small utility trench, Allied Rental Machines is here to back you with expert guidance, reliable rentals, and tailored maintenance solutions. Ready to power your project forward? Explore our full fleet and request a quote today: Contact Allied Rental Machines.
Have experiences or questions about earthmoving equipment? Drop a comment below or join our newsletter for insider tips and industry trends!
